Table of Contents
Looking back, we see so many changes in the Android Os names and features. From humble beginnings like supporting voice entry text support (2009), it soon progressed into a force to be reckoned with As it evolved, it produced more than quantity (with Google releasing updates almost routinely); its quality was also able to show. An example is the Android 2.3 Gingerbread, which allowed for multi-camera functionality (the ability to use more than just one camera) and soon-to-follow: support for multicore processors.
The Android has seen a long and hard road. But thanks to Google’s constant updates, it has progressed into a great smartphone. Tons of people use them in contrast to the iPhone, which is less capable of the constant updates the Android has seen. In fact, many have speculated that the iPhone has copied a lot of features produced by the Android! An example of this is in the Android 4.1 Jellybean.
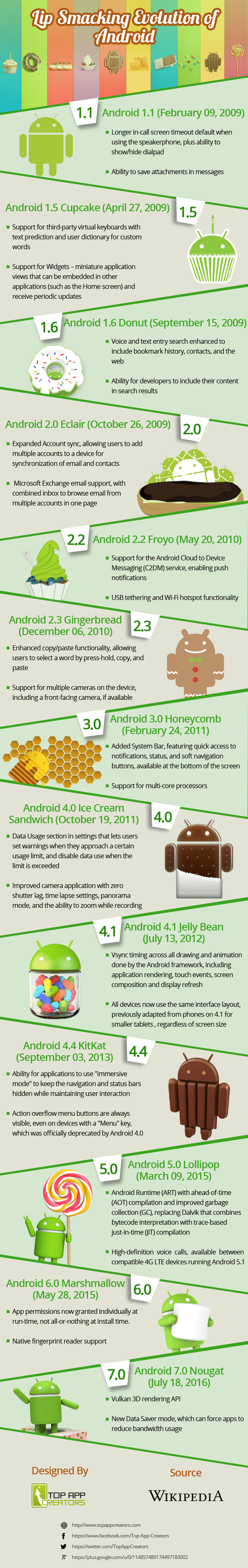
If you don’t have time to go through the entire article and find out Android OS names and release date here is an infographic by TopAppCreator which wraps almost everything about Android Version and features:
Android 1.0
It was practically the very first version . This software was published in September 2008. It was launched and available commercially to the wide consumer base via. the HTC dream.
Here are some of the features of Android 1.0:
- Android Market
- A website browser (with XHTML website pages, multiple pages shown as cards)
- Camera (although can’t customize the resolution). You can have a look at some of the best Camera Apps to Capture Photographs like Pro.
- having access to web email servers, supporting POP3, IMAP4, and Simple mail transfer protocol.
- Synchronization was definitely a large plus when the calendar, as well as the contacts sync, formed the basic base with this new version of Gmail.
- Google Maps. Here are 11 Tips to Customize Google Maps Effectively.
- Google Talk plus an impressive Bluetooth support were all welcomed.
These features become so popular-so and so fast. Thus, the android 1.0 laid a solid foundation for the versions ahead.
Android Petit-Four (1.1) (API level 2)
It was released in the month of February in ’09, this version premiered initially just for HTC dream. The android 1.1 resolved many bugs and introduced fixes on the glitches from the previous version,
More specifically, the android 1.1 brought along with many other features, namely:
- Longer in-call screen timeout while using speakerphone
- Enabling the consumer to save attachments in messages
- Marquee supports incorporated in system layouts.
Android Cupcake (1.5) (API level 3)
Then within the same year came the 1st version to officially utilize a code-name, ‘cupcake’. Released in the month of April 2009 and scaled like Linux Kernel. The code-name took it’s origin from a dessert.
From here on, that it was finalized that Android OS names will be using the codenames for the forthcoming versions could well be based on desserts.
The other functions it integrated included :
- The third-party virtual keyboards which offered user dictionary and text prediction.
- There was a different support for widgets, video recording, and playback in 3GP format.
- Copy and paste features inside browser were enabled within this version for the initial time. If you favorited a message, you may view their picture. Do you know you can Copy and Paste Multiple Text in Android!
- Animated screen transitions.
Android Donut (1.6) (API level 4)
Released inside the same year as it’s predecessor, this version scaled like the Linux kernel 2.6.29 together with many other functions :
- Searches associated with voice and text data entry were expanded to feature contacts, history, web services.
- Multi-lingual speech engine support.
- Ability to watch screenshots inside Android market.
- Tech supports for CDMA/EVDO.
- Support for WVGA screen resolutions.
Android Eclair (2.0) (API level 5)
Released in October 2009. Android Eclair came with certain amazing new updates and features.
The characteristics encompassed within this version of android included :
- Expanded account synchronization allowing users to incorporate multiple accounts into a device for syncing.
- MS exchange email support in addition to Bluetooth 2.1 support.
- Ability to locate all saved SMS cards, MMS messages within a conversation.
- The classy camera features such as flash, digital zoom, scene mode, white balance and much more.
- Refreshed browser UI with bookmark thumbnails and double tap zoom, in addition, to supporting for HTML 5.
- Improved google maps with all the newest version 3.1.2 together with MotionEvent class to hold an eye on multi-touch events.
Android Froyo (2.2 to 2.2.3) (API level 8)
Froyo, short for frozen yogurt was another version with the android operating system.
- This one witnessed an increase in memory, speed, and performance. If you are are an iPhone user then here is a tip to Improve iPhone Performance and Speed up your iPhone.
- Support for android cloud to Device messaging (C2DM)
- These had shortcuts to phone and browser apps and advanced launchers for applications.
- Updated android market.
- Support for upload fields within the browser.
Android Gingerbread (2.3 to 2.3.2) (API level 9)
This benchmark version premiered on 6th December 2010 and scaled like Linux kernel 2.6.35.
The features sustained by this version a variety of including:
- A highly impressive UI that has a simplistic design. Plus a native support for VoIP Internet telephony Featured an enhanced copy and paste functionality, allowing users to pick words by press-hold.
- NFC (Near Field Communication) was introduced in this version.
- A new download manager for easier file access.
- Improved power management along with concurrent garbage collection for better performance.
Android Honeycomb (3.0) (API level 11)
Released on 22nd February 2011 this SDK was the 1st tablet-only upgrade dependant on Linux kernel 2.6.36. Motorola Xoom tablet was the primary device making use of this SDK.
The features included:
- Holographic interface primarily to promote optimized tablet support.
- Added action bars and system bars.
- The keyboard was redesigned making the typing fast and efficient.
- More intuitive interface for copying and pasting.
Android Ice Cream Sandwich (4.0 to 4.0.3) (API level 14)
Based on Linux 3.0.1, this premiered in October 2011. This was a final version to officially support Adobe’s Flash Player.
New features included :
- Many advancements in Holographic interface with new Roboto font family.
- From Android 3.x, soft buttons have become available for use on phones.
- Separation of widgets in separate tabs.
- Drastic improvement in voicemail features. This change features to speed up or reduce messages.
- Integrated screenshot capture button along with better voice recognition. New unlock feature via Face recognition was added as a new feature too.
- Wi-Fi direct and 1080p video recording. Android VPN and TUN kernel module. Before this, the VPN required rooted android. Don’t forget to go through the article on how to Improve WiFi Signal Strength to get better speed.
- The succeeding updates included capabilities which weren’t a vast amount of significance.
Android Jelly Bean (4.1 to 4.1.2) (API level 16)
Launched in July 2012. This is dependant on Linux kernel 3.0.31 and it was a benchmark update.
The features included :
- A smoother UI with Vsync timing together with triple buffering.
- Bi-directional text and language support.
- The user was allowed to install offline maps.
- Notifications that can be Expanded.
- Ability to turn off or switch between notifications specific to applications.
- Bluetooth data transfer usage for android beam and also a multichannel.
Android KitKat (4.4 to 4.4.4) (API level 19)
This version hit the android market in September 2013. Initially, that they the codename Key Lime Android but the name was changed to kit-kat because hardly any people were aware of the real taste of the key lime pie.
This version was first launched on Google’s nexus 5 and was then later released with a wide variety of devices. Improvements in this particular project were known as Project Svelte internally by Google.
Minimum RAM requirement was 340 MB and all sorts of devices under 512MB were reported as low RAM devices.
The latest features include :
- All digits in clock became thin and the clock doesn’t show bold hours.
- Applications could trigger translucency from the context of navigation bars and status bars.
- Immersive mode to use by these applications to hold the bars hidden while interacting.
- The restriction was imposed on applications while accessing external storage, except while accessing their unique directories. However, you can download Paid apps for free.
- The performance was optimized to performed better on lower-end devices. Also, a part of them was the NFC host card which performed emulation, enabling the device to exchange smart cards.
- The Web views solely according to Chromium engine.
- There was obviously a public API for managing text messaging clients.
Android Lollipop (5.0 to 5.0.2) (API level 21)
Released with the codename “Android L” in March 2014. It was distributed as OTA, over-the-air updates for selected devices which ran on services by google, namely, nexus and google play edition devices in Google I/O.
- Featuring an attractive materialistic design along with a responsive language, Android Runtime officially replaced Dalvik for improved app performance, this is referred to as Project Volta.
- Android Runtime (ART) with ahead-of-time compilation through an improved garbage collection which replaced Dalvik.
- Support for 64 bit CPUS.
- Had an OpenGL ES 3.1 environment as well as an extension pack on GPU configurations.
- A refreshing looking screen without any longer support for widgets held by project volta for life of the battery. If you have forgotten your screen lock here is a hack to bypass Android Password/Pattern/Face/PI Lock!!
- Lock screen which gave shortcuts to apps and notifications. Guest logins and adding multiple user accounts were also included.
- Third party apps were again given the usage of read and modify data. DO you know you can Backup your Google Playstore Apps so that they can be installed afterwards without downloading them again.
- The addition of 15 new languages including Bengali, Basque, Chinese and more included.
Android Marshmallow (6.0 to 6.0.1) (API Level 23)
Marshmallow was released in May 2015. It was first launched on Nexus devices and before the end of year other devices too got the update.
Marshmallow introduced several changes that may have a significant impact. Some of them are:
- App permission model is opt-in (grant specific permission as requested) in lieu of opt-out (all is permitted, then use App Ops to perform off individual permissions).
- Power Conservation was focused (Doze mode) by allowing the product to go into hibernation when idle.
- Fingerprint sensor support is currently baked into the OS rather owner support, and USB C is currently fully supported.
- Allowed to format a microSD card and adopt it as an if it’s internal storage and share precisely the same internal security level. You can improve your Phone Internal Space without any software and if you are using iPhone here is an article to Increase iPhone storage space for sure without any software
Android Nougat (7.0 – 7.1) (API Level 24 –25)
It was introduced in July 2016 with Nexus to be the first device to receive the update.
Nougat introduced major changes to the OS and Development platform.
- Allowed multitasking by double tapping recent apps for quick switch between the recent apps.
- Allowed user to use two apps at the same time i.e adding multi-window mode.
- Added new animation and notification display.
- Major improvement over speed, memory, and performance.
- Added several new interface changes and modifications.
This was all about Android Versions and Names. The following chart compares the main difference between each android version and changelog:
Hope the article was informative and helpful to you. Stay tuned for more information. Also, don’t forget to share this article with your friends and let them also know about android history. You can also comment below and share your thoughts.






















